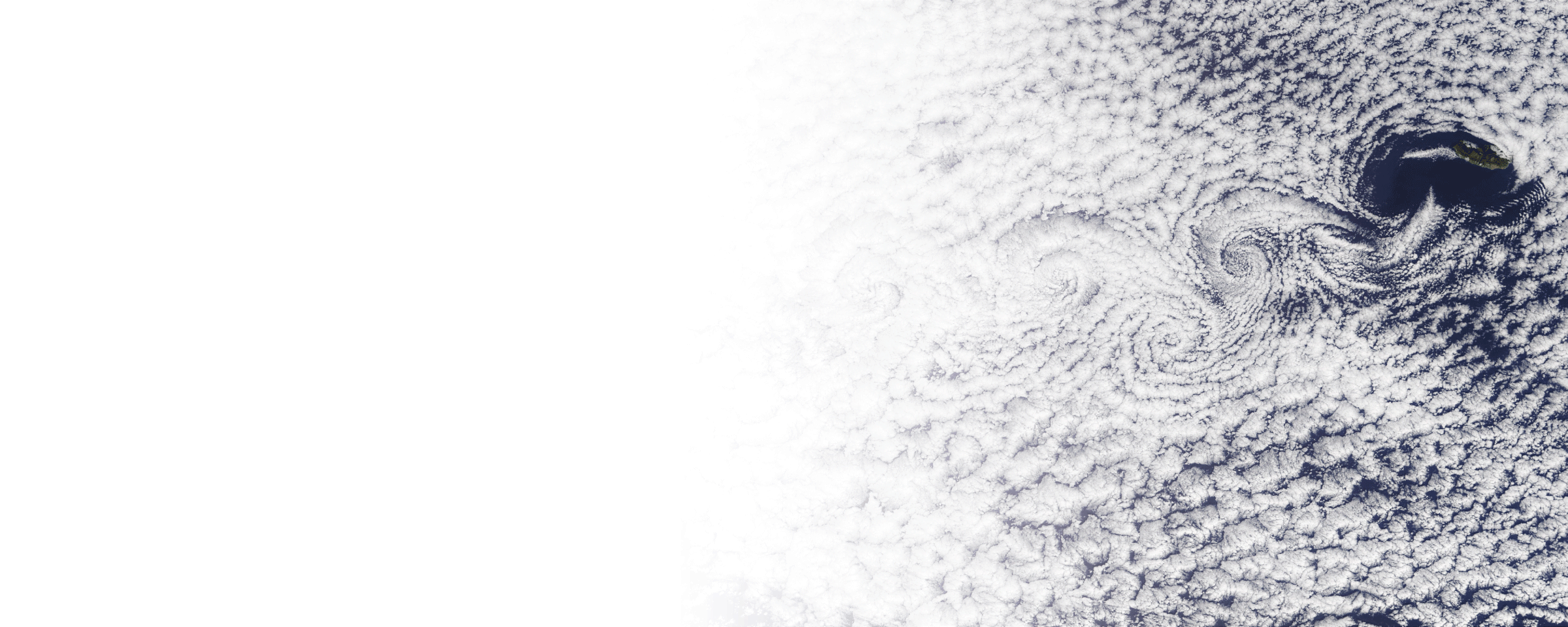
GAIN ACCESS TO A STRATOSPHERIC LABORATORY
Zephalto scientific flights integrate instruments for precise, direct measurements in the stratosphere. We support researchers from design to flight, with real-time monitoring and recovery of data and payloads.
GAIN ACCESS TO A STRATOSPHERIC LABORATORY
Zephalto scientific flights integrate instruments for precise, direct measurements in the stratosphere. We support researchers from design to flight, with real-time monitoring and recovery of data and payloads.

A UNIQUE LABROOM
Zephalto transforms the stratosphere into a veritable laboratory for high-altitude experiments. This enables in situ analysis of the climatic and chemical dynamics influencing atmospheric dynamics.
Access to it is essential to:
- Studying the impact of human activities,
- Refining climate change prediction models,
- Analyse changes in greenhouse gases.
MADE-TO-MEASURE EXPERIENCE
Our flight platforms offer prolonged and controlled exposure to the stratosphere:
- Up to 3 weeks
- Capable of reaching an altitude of 35km
- Nearly 2 tonnes of payload possible
- With a 2 Mbps downstream data flow

INTEGRATION TAILORED TO YOUR PROJECT
- Definition of technical needs with our engineers specialized in on-board instrumentation and pre-launch validation.
- Functional validation in real conditions with a pre-flight test report.
- Safe integration and transport of the payload before take-off.
- If required, real-time monitoring via data stream (2 Mbps), on-board video and balloon telemetry.
- Recovery and scientific exploitation, with transmission of environmental data and reconstruction of the flight trajectory.
USE CASES