GET A CLEAR VIEW OF THE STRATEGIC AREAS THAT MATTER TO YOU.
Our flights provide access to precise plot observation data, high-resolution images enabling the study of vast areas on a large scale. Act more efficiently, more cost-effectively and more sustainably thanks to optimum coverage and a level of detail available only in the stratosphere.
GET A CLEAR VIEW OF THE STRATEGIC AREAS THAT MATTER TO YOU.
Our flights provide access to precise plot observation data, high-resolution images enabling the study of vast areas on a large scale. Act more efficiently, more cost-effectively and more sustainably thanks to optimum coverage and a level of detail available only in the stratosphere.

OBSERVE, ACT.
Earth observation is a fundamental pillar of resource management, environmental monitoring and territorial security. At a time when climate change, increasing urbanisation and geopolitical tensions are redefining our priorities, rapid access to accurate data is becoming essential.
THE STRATOSPHERE: A STRATEGIC ZONE
Orbiting satellites provide a global view, but their frequency of passage, cloud cover and resolution can limit observation. Conversely, drones and aircraft offer detailed observation but cannot provide broad, persistent coverage.
The stratosphere represents the optimum compromise: it allows a global view without being subject to orbital constraints, while offering superior resolution and unrivalled flexibility.
A CHALLENGING ROUTE
However, access is constrained by technological, logistical and regulatory challenges, for which we deploy advanced systems and strict coordination with the aviation authorities.
Our stratospheric balloons are capable of operating at very high altitudes, in hostile environmental conditions (intense cold, low pressure, high UV exposure), while guaranteeing stability and control.
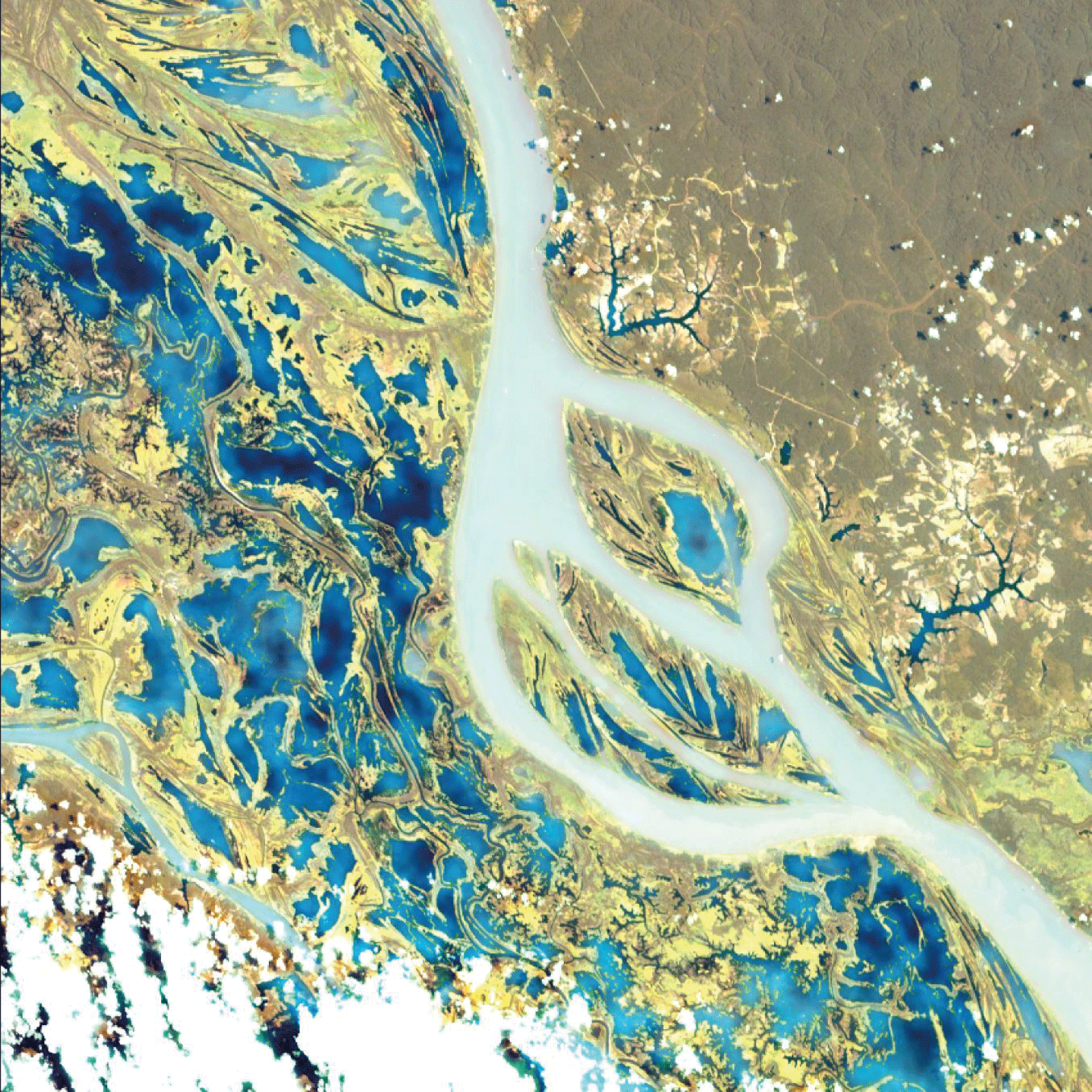
ACCURACY AND DETAIL
Our stratospheric balloons can reach altitudes of up to 35 km, above 98% of the atmosphere. This position offers ideal conditions for imaging and data collection:
On-board operator: Unique on the industry, the presence of an operator means that parameters can be adjusted in real time, ensuring optimum data collection.
Wide, precise coverage: At an altitude high enough to observe entire regions with finer resolution than a satellite.
Long-term observation: Unlike orbiting satellites, our balloons can provide long-term surveillance of a targeted area.
On-board hyperspectral and multispectral sensors: For detailed analysis of soil, vegetation, water and infrastructure, with unrivalled image quality.

USE CASES